HACCP - Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point
LAB-EL offer for the companies implementing the HACCP system
The LAB-EL company, offers to companies that implement HACCP, complex help including:
- preparing assumptions concerning quality system organization meeting the HACCP requirements in a certain plant,
- preparing a project for a measurement system for the technological processes needs GMP and HACCP,
- delivery, installation, start-up of a measurement system,
- preparing validation documentation of an implemented system,
- system validation in cooperation with an external accredited company, certifying the quality systems including HACCP.
In the end, full organizational, technical and training help is provided, ending with a certification of the HACCP system. The example implementation of the HACCP system in an army unit was introduced in a separate document.
Presentation of the HACCP system
Introduction
The HACCP was first evaluated in the early period of the American space flights program in order to assure microbiological safety of food for the astronauts. The system was evaluated (in the 60s) by the Pillsbury Company cooperating with NASA and the Research Laboratory of the US Army in Natic. Next the Pillsbury Company implemented the HACCP to its own food products and introduced this system to food industry.
Poland’s aim at integration with the European Union requires many adjustment actions, also spreading the rules of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice in food production) and implementation of the HACCP system in the food industry (European Directive 93/43/EEC concerning the hygiene of the food means).
The HACCP system is recommended by the WHO (World Health Organization), Codex Alimentarius and required by the legal system of the European Union. It is the most effective way of assuring high hygiene standard of the production conditions and food processing. The HACCP is a system procedure; its purpose is to identify the food heath quality hazards and the risk of their appearing, during all phases of a production process and food distribution. It is also a system, which controls and masters all hazards important from the point of view of a consumer safety and one’s health protection.
The HACCP protects the consumer interests providing one with a safety assurance and high health quality of the purchased food products. It also protects the producer’s interests, who conduct in an appropriate and documented way a production process can prove that everything possible is done in order to make a product, which is health safe. The Polish legal regulations require realization of the GMP rules in the whole food industry, group catering and food traffic. They also put a requirement of implementation of the HACCP system in the production plants that produce dietetic preparations and supplements. In the nearest future, as a result of the novelized legal acts (Act dated May, 11 2001 Dz. U. Nr 63, position 63. - art. 10 point 3, art. 28 point 2, art. 3, art. 32, art. 36 point 6 and art. 48 point 1 – where those regulations in the scope concerning the HACCP system are to be applied since January, 1) the HACCP system is going to become obligatory in all production and ford processing plants in Poland.
The concepts and definitions used in the HACCP
In order to effectively apply to the legal regulations and the problem associated with HACCP, one should define basic definitions that characterize the food industry and are a key to changes implementation of in every plant.
HACCP - (defined by the Codex Alimentarius) - Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point. It is a system designed for food safety control. Incorrect translation of the system’s name may lead to improper interpretation of its essence, which in reality is based on:
- analysis and prevention of microbiological, technological and chemical and/or physical hazards’ formation,
- its elimination,
- reduction,
- or intensification prevention – IN SUCH WAY THAT IT DOES NOT ALLOW ON PRODUCT CONTAMINATION.
HACCP is supposed to be used to minimize the risk hazards; it is then a prevention system.
HAZARD – it is every microbiologically factor, technological, physical and/or chemical, which can be a risk to consumer’s health.
RISK – it is a probability estimation of hazard occurrence.
CONTROL POINT – it is a place, an operation unit or a process in which a microbiological factor, chemical or/and physical can be controlled.
CRITICAL CONTROL POINT – it is a place, an operation unit or a technological process in which one should apply the control means in order to prevent, eliminate or minimize the accepted level of hazards for food safety.
An additional characteristic feature is that they are (CCP) under (permanent) control for each one of a product’s series.
Some sources inform that it is possible to distinguish CCP when concerning:
a) degree of hazard elimination
b) degree of hazard for a final quality of a finished product.
DECISION TREE - it is a sequence of information used for stating whether a certain control point is critical.
CRITICAL LIMIT - it is a criteria (see the example graph), which has to be fulfilled (cannot be exceeded) for each protection mean, associated with a certain critical control point.
OPERATIONAL LIMIT - it is a criteria more strict than a critical limit and is used in a technological process as a process value (see the example graph) in order to reduce a risk of deviations in a certain critical point.
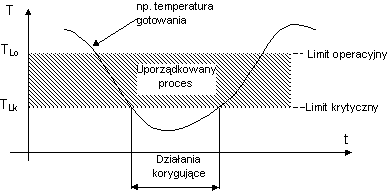
DEVIATION - it is stating inability of keeping a process in the set limits for a certain critical point. A decision making moment concerning further wareabouts of an undertaken process.
MONITORING - it is a planned and systematic check, through observation and/or measurements in order to state whether a certain critical point does not “escape” from under control. In a monitoring process adequate entries and/or registry take place, in order to allow realization of later analysis and/or verification.
CORRECTION ACTIONS - they are procedures of proceeding in case of critical limits exceed in a certain critical point. Those actions should be performed in order to eliminate the causes of incapability and their effect should be stating the prevention means that have to be undertaken in the future so a similar situation does not take place again. All those actions have to be adequately documented in process and finished with an adequate protocol, which will be a base for changing the HACCP plan.
PREVENTION ACTIONS - the actions that are supposed to eliminate the causes of inconsistencies after their appearance and help realization of the correction actions (but not their results). An effect of those actions should be an elaboration of improvements protecting a process against a repeated appearance in the next series of a ready product.
RISK - stated in a written form probability of hazard appearance in a certain production process.
CONTROL UNIT (MEASUREMENT) - includes all devices and personnel actions that are supposed to specify the limits of an undertaken process and allow on elimination of safety hazards of a ready product, possibly based on them it is possible to state that the process was kept within the boundaries of accepted hazard limits.
HACCP PLAN - a document stating the methods, the prevention means and the course of actions that should be undertaken in a certain production process in order to control the hazards for quality of a food product.
VALIDATION - a proof carried out proving that the majority of planned actions, devices, rooms and personnel actions in a certain production process leading to expected quality results.
SYSTEM OVERVIEW - periodically undertaken check actions, realized by the management. Those actions have to be documented and the effects and conclusions should help when modifying the system in the future.
FOOD HYGIENE - all actions required in order to assure safety and quality of healthy food, covering all forms that appeared before (i.e. harvest, crop, general product gaining) during a basic production (storage, technological actions, maintenance, packing etc.) as well as after it i.e. transport, marketing elements etc. In reference to this definition another concept was coined – HEALTHY FOOD – all food articles in the stages from raw materials up to a moment of sale to a client regulated by HACCP and producer supervision, where their parameters are adequate for consumption to people from the point of view of hygiene.
HACCP in international, European and national legal regulations
At present, functioning of the regulations concerning the rules of food production can be named as Food Law, which only in small degree differs between particular countries and in one is the same everywhere – in treatment and rank of the HACCP regulations. Generally they can be defined as a system of legal standards that set the standards of producing and rotating the raw products, food products, stimulants and objects of use that are in contact with them in the scope necessary for health protection and meeting the consumers’ expectations.
In the USA
In the years 1972 - 1978 the Food and Drug Administration introduced obligatory in food production realization by the producers the HACCP regulations (first regulation - 1973 – concerned the producers of canned food of low acidity). In time individual elements of food industry were in the following years covered by those regulations. Practically ever since 1979 it can be said that all products covered by Food Law are a standard for each producer registering its product.
In EUROPE
In the European Union the producers tried to realize the HACCP programs since the middle of 1975. Individual member countries with a few years delay unified the regulations concerning the quality system in food production with the FDA regulations.
>From the legal acts issued since that time fundamentally important are: the Counsel Directive number 89/397/EWG dated 14.06.89 concerning official control of food articles. It was stated in there that the most important aspect is the protection of human health. Another important element is that it provided a lot details concerning control (inspection), sample taking, analyses and documentation.
Another important document is the Council Directive number 93/43/EEC dated 10.06.93. It defines beside obligatory application in production of the HACCP regulations the role also the requirements concerning hygiene, purchase, distribution and food sale. Another important element of that Directive is stating that persons who work on a food market should analyze each critical step in their actions in order to assure food safety and confirm that they use adequate dealing procedures in standard procedures during business operation. In order to characterize various groups of food, state their specific features, separate regulations were issued concerning meat, fish, eggs, milk and other. An example from fish branch: the Directive number EEC 91/493 dated 22.07.91 concerning international health control of the fish products and the decision of the EC Committee number 94/356 dated 20.05.94 stating detailed rules of applying the Directive number 91/493.
The EU countries since 01.01.99 have to apply in the food production plants all mentioned above Directives along with the branch supplements.
In POLAND
In Poland, a problem of food quality production was presented within the legal frames for the assortment of diet food means, diet supplements and supplements by the Minister of Health in year 1996 (Order MZiOS dated 22.08.1996, (Dz.U. number 108, position 520) - paragraph 5: “Production internal control should be set basing on a system of critical control points (HACCP), after settling it with the appropriate national (provincial) sanitary inspector. Such legal regulation will probably be extended and cover left food assortment within a few years. The producers of food means independently started or are planning on implementing the HACCP system in the nearest future.
The Act dated May 11, 2001 concerning the food health conditions (Dz. U. Nr 63, position 634 with the change dated October 30, 2003 Dz. U. 208 position 2020) makes the HACCP system obligatory in all production and food processing plants in Poland independently from their size.
The HACCP system requirements
The HACCP is a system, which identifies estimates and controls all food safety hazards. It can be in short described as a system of assuring food safety.
The traditional way of testing ready products, based on random sample collection from a random lot of ready products, does not guarantee its safety, because the probability of detecting a lot of product, which can cause damage to a consumer’s health, amounts to only few percents.
The limitations of the traditional inspection of a ready product quality result among other from the test imperfections for hazard detection (i.e. limited selectiveness, sensitivity and repeatability). Small effectiveness of the traditional quality control results also from impossible to be judged placement of hazard in a mass of product and random appearance of health hazards in a lot of product. Such system limits itself basically only to quite random detection of a hazard, without any interference in the causes of their appearance, except from the group occurrences of food poisoning. In the HACCP the main pressure associated with supervision over food is put on the causes of hazards immediately in a place of their formation (also during storage and transport). Because of such approach, before a good is produced the health hazards associated with the raw materials, additions and supportive materials, personnel, machines and devices as well as technological process are prevented or eliminated. It is the most effective way to guarantee food safety acknowledged by all the organizations interested with its safety.
The system requirements of hazard analysis and critical control point were compared in 7 rules setting the guidelines for evaluating, implementing and maintaining the system. They were prepared in such a way so they could be applied in all sectors of food industry. Those rules obtained international recognition and the details concerning their usage were published by the Committee of Food Codex (FAO/WHO) and the National Advisory Committee dealing with the Food Microbiological Criteria (NACMCF).
The HACCP system rules
Rule no. 1: The hazards’ identification and description of the prevention means
A team should be created, which is going to be responsible for all actions undertaken during a system creation, implementation and maintenance. A block scheme should be created of a technological process and after its verification all possible hazards ascribed: biological (bacteria, viruses, parasites), chemical (natural toxins, chemical compounds, pesticides, heavy metals, leftovers of the washing agents) and physical (glass, metal, casing’s elements) occurring on its individual stages and associated with the raw materials used, additions and materials. Next the importance of hazards should be estimated and the control means described allowing on controlling the important food safety hazards.
Rule no. 2: Identification of critical control points
The HACCP team should identify the so called critical control points (CCP), understanding all places in a technological process, in which for assuring food safety control it is obligatory in order to control the occurring hazards. For CCP identification it is recommended to use one of many of the so called decision trees.
An example of the decision tree:
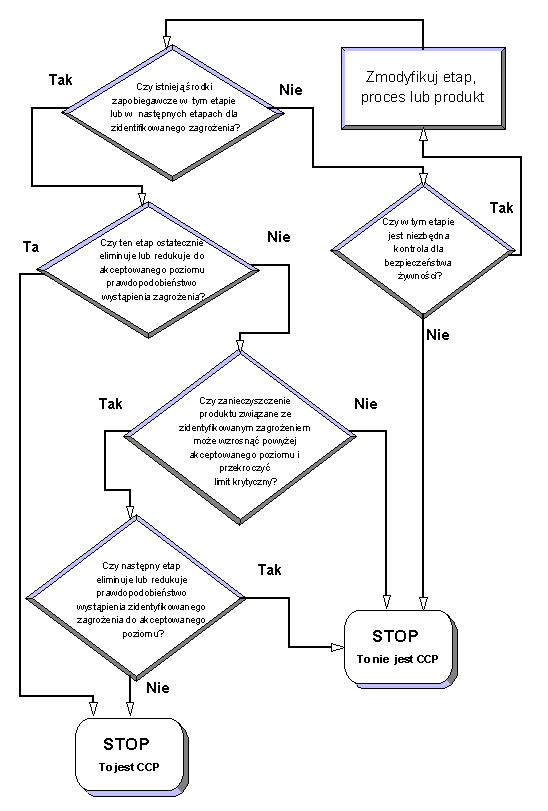
Rule no. 3: Critical limits identification
For each CCP the so called critical limits (thresholds) should be settled, naming such measurable values of the control means that cannot be exceeded, because it is unambiguous with loss of a ready good safety.
Rule no. 4 settling the CCP monitoring system
Each CCP should have settled the requirements regarding the way and frequency of readout and recording of the control means values (so called CCP monitoring) and a person responsible for those actions.
Rule no. 5: Defining of the correction means
The correction action procedures should be created that have to be undertaken when monitoring shows exceeding set critical limits. It is also necessary to assign a person responsible for undertaking those actions. The correction actions should include a way of restoring the hazards’ control in CCP, as well as a way of proceeding with a product, which was produced when the set critical limits were exceeded.
Rule no. 6: Settling the entries procedures
A way of checking the system functioning accuracy should be described. Such system described in a form of a procedure can be based on the results from the microbiological testing of the final products or complaints. A recommended way of system verification is performing the so called internal system audits.
Rule no. 7: Settling the system verification procedures
Documentation and entries of the HACCP system are a proof for assuring food safety and that is why the procedures of creating, keeping, storing and supervising all the documents and entries of the HACCP system should be created.
The necessity of implementation of the HACCP systems
The necessity of implementing the systems of assuring safety of the food means results from many factors, such as: food safety, consumer requirements, legal regulations, losses caused by food poisonings and internal and external trade. From the mentioned above factors the most important is the necessity of eliminating the health hazards or human life.
The human life is the most important value and that is why it should be the basic cause of propagating and implementing the HACCP system, as it is the most effective way of assuring food safety. Beside health protection of a consumer another important aspect of food safety is its influence on a country’s economy. As an example of the size of damages resulting from unbalance in food safety one introduce the BSE disease in the European Union. The losses caused buy this disease are estimated to tens of billion of euro and its results are going to be felt in many countries still in the years to come.
The consumers of food means are one of the most important elements of pressure on the food producers, because it is their needs and preferences that decide about sale quantity and a modern consumer knows his legal rights, especially when it comes to access to safe food. In pursuit of meeting a consumer’s needs in the scope of food safety, the hypermarket networks that operate on the territory of Poland require from their suppliers of food products implementation of quality assurance systems of assuring also its safety (HACCP).
The legal national and international regulations that concern gaining, processing and food rotation put on the food producers an obligation to implement the HACCP system.
From among the economic means that speak on behalf of the necessity of applying the HACCP system, one should mention the losses that come into existence as a result of food poisonings. The costs of such poisonings cover the costs resulting from among other: treatment of people, necessity of withdrawal and/or destruction of the goods from the market, absence at work, additional tests performed by the food supervision staff. In extreme cases even a production plant may have to be closed down.
In recent years in Poland one can observe the intensified interest of various companies with the system of quality assurance in production, according to the requirements of the norm series ISO 9000. Increasing from year to year a number of companies that have certified systems of quality, functioning according to the norms series ISO 9000 involves the necessity of meeting the requirements that the companies offer its contractors. Such companies are interested especially in cooperation with the producers of the food means that have implemented the HACCP system. The contractors that do not have any system of guaranteeing the quality of their products have serious problems with selling their goods, what can become even a bigger problem after admitting Poland to the European Union.
The last economic factor that compels the necessity of implementing the HACCP system is international trade, especially in the countries from the European Union. All European Union member countries are open only to safe food. After the spectacular cases of trust weakening in food safety in few of the European countries, the boundaries of those countries were effectively sealed against imported food. In such situation the HACCP system, which functions in an organization is a necessary condition when exporting the food means to the countries of the European Union.
When it comes to an organization’s management, the implementation of the HACCP system should be treated as an investment, which in the near or later future is going to return the suffered costs.
Implementation and maintenance of the HACCP system assures food full safety guarantee, what results in many measurable benefits for an organization i.e. easier commerce on a national and international market, bigger chances for keeping old and gaining new consumers.
In an organization with an implemented HACCP system, the scope of employees’ responsibilities is clear, what improves work organization and utilization of the resources (raw materials, machines, people) leading to lowering general production costs. Because of lowering frequency of performing the internal operation tests and also of ready goods there is further possibility of lowering the production costs.
The mentioned benefits are typical for the majority of organizations and in a final settlement they cause a few percent increase in profit. There are of course also other benefits resulting from individual corporation conditions.
The measurement systems realization for HACCP
The HACCP system, which main and the most important aspects were introduced in the previous part of the article, concerns generally food safety in the scope of productivity, processing, storage, transportation, it systematizes the roles of conduct when checking and defining the critical points for each provided process in a certain filed of hazard occurrence. In order to prevent the hazards one has to get to know them, and more specifically speaking, measure their specific features in the critical control points (CCP). Each production process has its own specific and technological subtleties that result in individual approach, sometimes different for apparently similar phenomena. The HACCP system does not impose stiff, unchangeable rules; it only specifies the rules of conduct. It requires, however some integrity and systematic, thanks to which the hazard prevention will be most effective.
The hazards that one has to take into account, when analyzing the critical control points (CCP), are as mentioned before:
- biological hazards,
- chemical hazards,
- physical hazards.
All of those hazards can come from:
- raw materials,
- technological process,
- environment (machines, production plants, elements that come into contact with food, etc.),
- water and air,
- directly from the personnel.
In cases when probability of hazard occurrence is high, it is called a meaningful hazard and unconditionally has to be controlled. Defining the meaningful hazards is associated with specifying the prevention means.
The prevention means for the biological hazards are:
For the chemical hazards they are:
- raw materials control,
- technological processes control (production),
- additions control.
For the physical hazards they are:
- raw materials and suppliers control,
- control during production (i.e. using the magnets, metal detectors, etc.).
Usually the control is applied to the parameters that can be easily and in a fast way measured during a lasting technological process, such as:
The LAB-EL company specializes in production and apparatus application as well as control measurement systems realizing the measurements, registry, analysis, regulation, signaling the exceeds of threshold values (limits) and keeping data archives of such physical values as: temperature, humidity, pressure (absolute and differential), CO2 concentration analysis, all meteorological parameters (i.e. precipitation, wind speed and direction, etc.) and other according to the clients’ requirements and wishes, specific for a certain technological process.
The company has huge experience in control of the climate parameters in the food production halls, depots, warehouses (also of the food means), realizes climate control in the mushroom cultivation halls and the greenhouses based on huge application experience. The measurement results and exceeds of the critical limits can be registered for the verification – identification purposes (according to the HACCP system requirements concerning the event records), and the values of measured volume, logical exceed conditions, critical and operation limit values can be monitored locally and/or remotely through radio communication (cellular telephony) of the Internet.
The features distinguishing the offered measurement systems are:
- measurement accuracy, device reliability, simplicity of use,
- remote measurement of climate parameters, digital transmission, central readout,
- digital registry of the measurement results,
- easy transfer of the measurement results to a standard PC computer,
- signaling the exceeds in set alarm thresholds (critical limits),
- emergency conditions signaling,
- system modularity, possibility of later expansion,
- 24 months warranty,
- full after warranty service.
The measurement - registry systems LAB-EL are among other, exploited in:
- production rooms and the production plants’ warehouses (especially the food branch),
- pharmaceutical warehouses store rooms,
- epidemiological-sanitary stations,
- quality control laboratories,
- meteorological laboratories,
- army units’ warehouses,
- churches and museums (monument protection),
- companies applying the standards series ISO-9000 and HACCP.
Especially the apparatus and the LAB-EL company systems find application in all of the plants implementing the standards series ISO-9000 and HACCP, since the devices’ technical parameters and enclosed to the devices calibration certificates meet adequate requirements.
A proof of high meteorological and usage quality of the devices produced by the LAB-EL company are received certificates and quality certifications:
- certificate of type from the Central Office of Measures for the hytherographs,
- individual certificate of calibration from the laboratories:
- an option of subjecting the meters for periodical calibration in the accredited laboratories.
The LAB-EL company does not limit itself only to products offered at present, but it is open to constant development as a proof of what one can mention the development of a universal microprocessor regulator LB-600, which thanks to its library of the following algorithms: measurement, alarm, control and regulation, time-binary, and other allows on tracking and registry of many physical quantities processed to a standard analogue and/or digital signal. The regulator can receive the signals from the following sensors: pH-metric, conduct metric, magnetic, optical and other that measure and/or signal the values monitored in the critical points defined based on the principles formulated by the HACCP system.
The full LAB-EL offers along with the devices’ basic technical data are available in the Internet on the web site: http://www.label.com.pl
Additional information about the HACCP system can be found on the web sites: Guidebook for the Preparation of HACCP Plans and Generic HACCP Models, Pathogen Reduction/HACCP & HACCP Implementation, The International HACCP Alliance.


